OpenShift Logs to AWS with Amazon OpenSearch: Enterprise Log Management Transformation for MBH
A Case Study on Cost-Effective Hybrid Cloud Logging Architecture
MBH Bank successfully transformed its enterprise logging infrastructure by migrating from on-premises OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) to a hybrid AWS cloud solution, achieving significant cost reductions while maintaining operational excellence. Working closely with AWS Advanced Consulting Partner TC2, MBH Bank implemented a two-phase approach: first, establishing a proof-of-concept with AWS CloudWatch Logs, then optimising costs by migrating to AWS Managed Streaming for Kafka (MSK). This initiative fits into a broader enterprise strategy focused on leveraging cloud managed services while keeping sensitive workloads under strict governance. The hybrid approach ensured flexibility without compromising control, a critical factor for regulated financial institutions.
The project demonstrates the power of AWS’s comprehensive logging and analytics services, delivering a 70% cost reduction in log processing while improving scalability, reliability, and analytics capabilities. This transformation showcases how traditional financial institutions can leverage AWS’s cloud-native services to modernize their infrastructure while maintaining strict security and compliance requirements.
Key achievements include: 70% reduction in log processing costs, seamless integration between on-premises and AWS environments, enhanced log analytics capabilities with Amazon OpenSearch, improved operational visibility and monitoring and scalable architecture supporting future growth.
Business Challenge
MBH Bank faced significant challenges with its existing on-premises logging infrastructure. As a leading financial institution, they generated massive volumes of log data from their OpenShift Container Platform, requiring centralized management, analysis, and long-term archival capabilities.
Regulatory and operational pressure points
Operating a complex banking environment on-premise OpenShift also introduced challenges related to scalability and maintenance. As application workloads grew, the limitations of the existing logging approach became more visible, increasing the effort required to ensure consistent observability across teams and environments.
A key difficulty was operating a legacy setup built around on-premise OpenShift, which made it increasingly complex to design a future-proof centralized logging architecture AWS could support at scale. This setup limited flexibility while increasing operational overhead.
Technical, operational and compliance requirements have been collected. For example, an increase in log size, that is, exponentially growing log volumes from containerized applications. Additionally, there was the challenge of managing and analysing distributed logs across multiple environments, as well as a requirement for near real-time log analysis and alerting. From the cost side, there was a need for cost-effective long-term log storage and processing. In addition to all this, there were regulatory requirements for log retention and auditability.
The bank required a solution that could handle its current 1 Gb/s Direct Connect bandwidth while providing room for future growth, all while maintaining the highest security standards expected in the financial services industry.
Initial Solution
Working with TC2, MBH Bank implemented a comprehensive proof-of-concept leveraging AWS’s native logging services. The initial architecture demonstrated the feasibility of hybrid cloud logging while establishing the foundation for future optimizations.
Hybrid validation phase with Amazon OpenSearch and CloudWatch Logs
During this phase, CloudWatch Logs served as a validation tool, demonstrating that hybrid ingestion from on-premises environments could meet performance, reliability, and compliance expectations without disrupting banking operations.
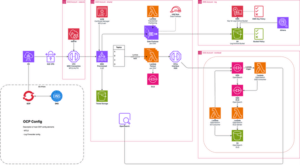
The initial solution utilized AWS CloudWatch Logs as the central log aggregation service, with Amazon OpenSearch providing advanced analytics capabilities. The architecture included the network infrastructure (Direct Connect, VPC Endpoints, Network Firewall), as well as the data processing pipeline (CloudWatch Logs, AWS Lambda, Amazon SQS, Amazon OpenSearch, Amazon S3).
The initial architecture successfully demonstrated the seamless integration between on-premises OpenShift and AWS services, the reliable log delivery and processing at scale, the advanced analytics capabilities through OpenSearch, and the operational improvements in log visibility and management, taking into account compliance with financial services regulatory requirements.
Evolved Solution Architecture for Centralized Logging Architecture AWS
Following the successful initial phase, MBH Bank and TC2 identified a critical optimization opportunity. While the CloudWatch Logs solution proved technically sound, the massive volume of log data resulted in unexpectedly high operational costs because of the CloudWatch Logs ingestion costs scaled linearly with data volume, high-frequency log generation from containerised applications, and substantial costs for log storage and processing.
Cost-driven architectural redesign
The shift toward a centralized logging architecture AWS approach enabled MBH Bank to decouple log ingestion, processing, and storage. This architectural flexibility not only reduced operational costs but also allowed independent component scaling, ensuring the platform could adapt quickly to changing business and regulatory demands.
Replacing CloudWatch Logs ingestion with streaming-based processing enabled a redesigned centralized logging architecture AWS environments could operate at significantly lower cost, without sacrificing throughput or resilience.
The high costs threatened the long-term viability of the cloud logging solution, requiring immediate architectural optimisation while maintaining all existing functionality and performance characteristics.
TC2’s cloud architects designed an innovative cost-optimised solution utilising AWS Managed Streaming for Kafka (MSK) as the primary data ingestion layer, dramatically reducing costs while enhancing scalability and reliability.
The evolved solution replaced expensive CloudWatch Logs ingestion with a sophisticated streaming architecture built on Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka, resuting in a high-throughput, low-cost log ingestion solution.
The process involves a new, advanced data flow: the on-premise OpenShift logs stream directly to AWS MSK topics, then a Lambda consumer processes MSK messages, and Kinesis Data Firehose delivers the processed logs to S3 with automated compression and partitioning and lifecycle policies for cost-optimized storage.
Measurable business impact
Beyond infrastructure metrics, the transformation delivered tangible business value. Faster access to log data improved root-cause analysis, reduced mean time to resolution, and supported proactive issue detection. These improvements contributed directly to higher service availability and a better overall customer experience.
Conclusion
The successful transformation of MBH Bank’s logging infrastructure demonstrates the tremendous value of AWS’s comprehensive cloud services when implemented by experienced partners like TC2. This project demonstrates how traditional financial institutions can utilise cloud-native technologies to achieve substantial cost savings while enhancing operational capabilities.
By moving away from on-premise OpenShift dependencies and aligning the initiative with a broader cloud migration strategy, MBH Bank created a scalable, compliant, and future-ready logging foundation.
This case study serves as a blueprint for other financial institutions seeking to modernize their infrastructure while maintaining the highest standards of security, compliance, and operational excellence. The partnership between MBH Bank and TC2, powered by AWS’s industry-leading cloud services, has created a foundation for continued innovation and growth in the digital banking era.